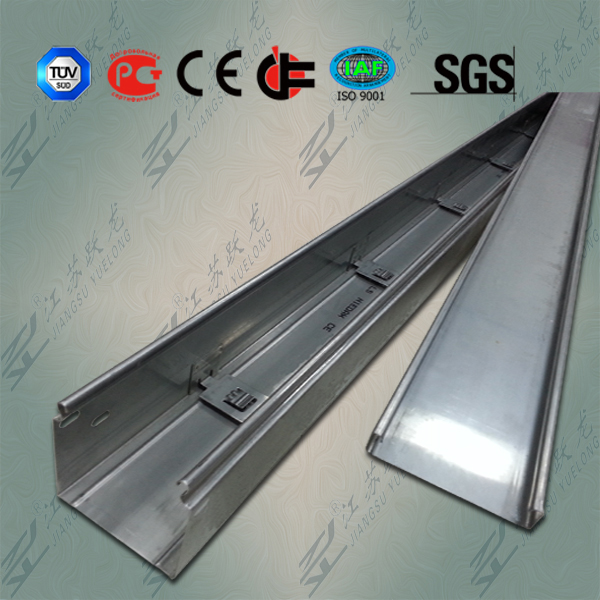
Cable trays adapt to changing needs
Cable-tray systems comprise sections and associated fittings that form a rigid structural distribution system to support cabling within a building. Cable trays are often preferred to conduit and raceway systems because of their accessibility and ability to accommodate change. Changing cables is easy because cables can enter or exit the trays at any point in the system. The open construction lets you see if there is enough capacity left for additional cable and also facilitates inspection of the cable and cable trays.
The difference between cable trays and raceways, according to Frank Casteel, vice president at Mono-Systems Inc. (Rye Brook, IL), is that "raceways are generally mounted on a wall in a room where power and communications cables are terminated. Cable trays are usually overhead or under raised floors but the wiring is open. They are used to distribute cables from the source to the point of use. There is no facility, however, to terminate the cable inside the tray."
Choosing a cable tray
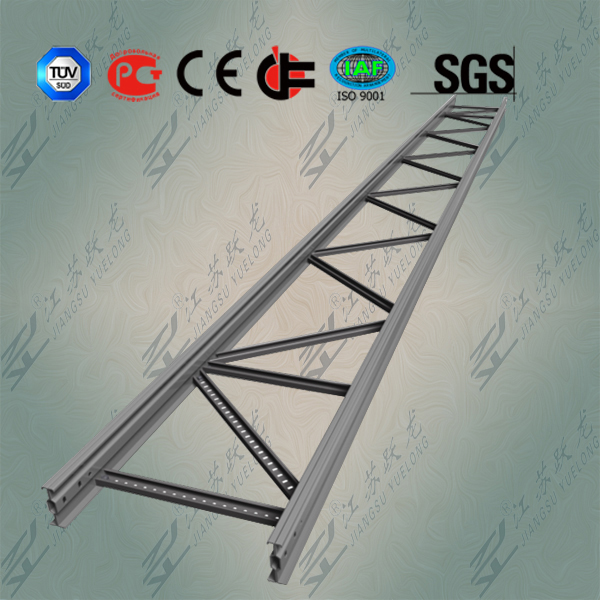
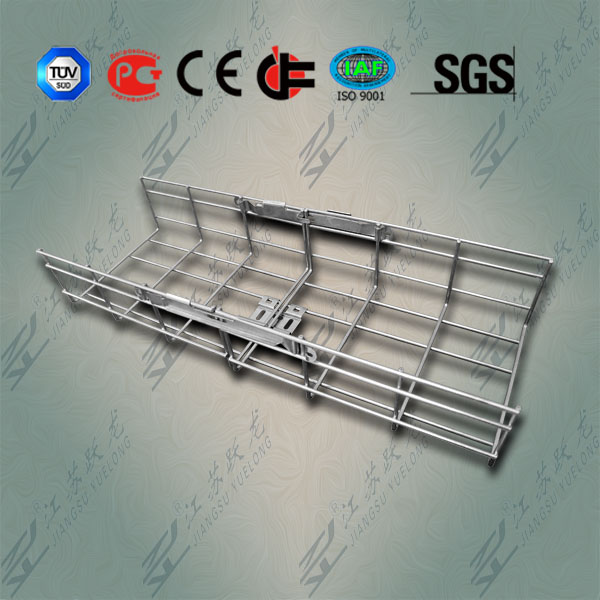
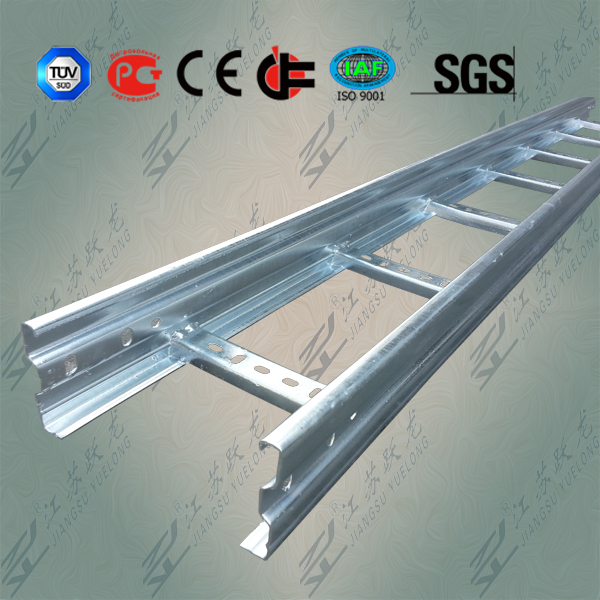
The basic types of cable trays available are channel, ladder, solid-bottom and trough. Other versions of these basic designs include single-spline and open-mesh construction. The engineer or designer will usually specify the type of cable tray that has the features to suit the project. "It depends on the situation and the environment," says Jay Burke, project manager at Sullivan & McLaughlin Communications Group Inc. (Quincy, MA). "For example, for larger bundles or heavier cables, I would recommend a ladder tray."
The ladder cable tray has two side rails connected by cross members, or rungs. This type of cable tray is effective because the ladder rungs give you easy accessibility to the cables, from the top or bottom. The rungs also provide convenient anchors for tying down the cables.
Kevin Smith, project coordinator at MTS Services (Bedford, NH), agrees that "typically, cable trays are going to be in an environment where changes are happening all the time. The ladder type would go either in a main or intermediate distribution frame closet or above a ceiling, because that`s more permanent."
A trough cable tray is a prefabricated structure consisting of a ventilated bottom with side rails. The ventilated trough cable does provide more support to cables than the ladder type, but this additional support is not significant. One reason you might choose the trough cable tray is for aesthetics--no drooping of cables.
For fiber-optic cable installations where drooping of cables may affect system performance, solid-bottom (non-ventilated) cable trays are preferred. However, the main reason for selecting solid-bottom trays is the concern for electromagnetic/ radio-frequency interference protection, or for sensitive circuitry. In addition, local building codes may require enclosed cable-tray systems under certain conditions. The designer, therefore, may choose solid-bottom cable trays, usually with covers, to provide shielding.
The channel cable tray is a section with a one-piece bottom. It is usually no wider than 6 inches, and may be ventilated or solid. "Not much channel cable tray is used," says Casteel. "It`s nothing more than a metal tray that can be used for very small cable installations."
The decision to use cable trays is dependent on the project. Where building codes permit telecommunications cables to be placed in suspended ceiling spaces without conduit, these pathways usually consist of cable trays. Another method used for routing equipment cable to the crossconnect is under a raised floor.
"In a dropped ceiling or under a raised floor, in many cases, is classified as plenum air space," says Sandy McWilliams, manager for fiber-optic products at ADC Telecommunications (Minneapolis, MN). "In a plenum space, it is important to use a plenum-rated cable-tray system. Also, installers have to comply with building codes, which dictate the cable type to be used in an open or closed plenum cable-tray system."
Overhead or under raised floor
Overhead cable trays are the most common for routing equipment cable to the crossconnect in large equipment rooms. They may also carry backbone cables to the backbone path. Cables should not be allowed to rest directly on ceiling panels and must be suspended from or attached to the structural ceiling or walls with hardware specifically designed to support their weight. When you install the cable trays, be sure to coordinate the tray locations with lighting, air-handling and fire-extinguishing systems so that the trays will not obstruct these operations. Leave sufficient space to permit adequate access for installing and maintaining the cables.
Some advantages of a ceiling cable-tray system are that it provides a flexible way to distribute cables to workstations, cable lengths can be kept to a minimum, and cabling can be easily changed or added, with minimum disruption to tenants. The disadvantages are that ceiling systems are inaccessible over plaster or spline ceilings or sealed air plenums, and the cables may pick up noise interference from electrical fixtures or wiring.
When the equipment room serves both computer and telecommunications equipment, you might use an under-floor cable-tray system. With this type of system, you should ensure that you avoid cable congestion, provide enough cable slack and allow for access to the cables.
"We would not recommend cable trays for under-floor use because you`re not really providing any protection for the cable," says Smith. "And for fiber-optic cable, we prefer to enclose it in innerduct."
However, some manufacturers recommend that fiber-optic cable should be run in cable trays to avoid tension, crushing and bending. "The most important issue is to ensure that the bend radius for the fiber-optic cable is maintained within the standards," says McWilliams. "What we recommend is that you manage fiber-optic cables separately because of the crush loads of the heavier copper cables."
Information about
- Cable tray installment
- Cable tray selection
- How to see the cable tray layout whether qualified
- Non-metallic cable tray
- Cable tray market capacity is big
- Advantages of using cable trays instead of conduit
- Choosing right cable tray
- How to choose cable tray
- Cable tray type selection
- What is the function of ladder cable tray?
Hot Sale
Top articles
- Cable tray installment
- Cable tray selection
- How to see the cable tray layout whether qualified
- Non-metallic cable tray
- Cable tray market capacity is big
- Advantages of using cable trays instead of conduit
- Choosing right cable tray
- Cable trays adapt to changing needs
- How to choose cable tray
- Cable tray type selection
Latest articles
- The case of Russia Heidelberg Tula
- Cable trays adapt to changing needs
- The case of Qilian Mountains cement factory
- Advantages of using cable trays instead of conduit
- The case of Huarun cement factory
- What is cable tray?
- Cable tray selection
- The case of Lafarge group
- What types of cable tray are available?
- The case of Lafarge in Ruiangong